Breast Cancer Doctor in Delhi
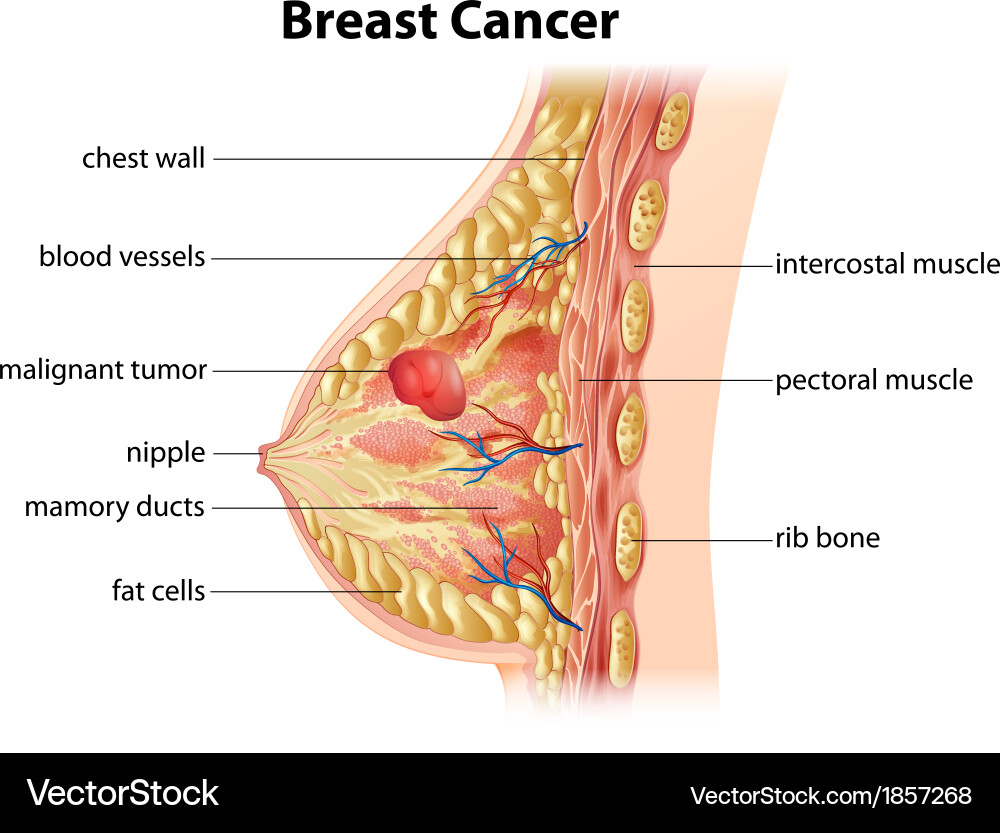
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that forms in the cells of the breasts and is one of the most common cancers affecting women, though it can also occur in men. It often begins with a lump or abnormal tissue growth, which can be detected through screening methods like mammograms. The exact cause is unknown, but factors like age, genetics, hormonal influence, and lifestyle choices can increase the risk. Symptoms may include lumps, nipple discharge, changes in breast shape, or skin dimpling. Early detection plays a key role in treatment success, which may involve surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or hormone therapy.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of breast cancer is not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified:
Inherited changes in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 significantly increase the risk.
Having close relatives with breast cancer increases the likelihood.
Risk increases with age, particularly after 50.
Early menstruation, late menopause, hormone replacement therapy, or having children later in life may contribute.
Smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle are linked to higher risk.
Past exposure to radiation therapy, especially to the chest area, can be a risk factor.
Common Symptoms
Being aware of the signs of breast cancer can lead to early detection, which is crucial for successful treatment. Common symptoms include:
- A new lump in the breast or underarm
- Swelling or thickening in part of the breast
- Irritation or dimpling of the breast skin
- Redness or flaky skin on the nipple or breast
- Nipple discharge other than breast milk, possibly including blood
- Change in the size or shape of the breast
- Pain in the breast area
Diagnosis
Breast cancer diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical exams and imaging tests:
- Mammogram: An x-ray of the breast, often used for early detection.
- Ultrasound: Helps distinguish between solid tumors and fluid-filled cysts.
- Biopsy: The removal of a small sample of breast tissue for laboratory testing.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of the breast.
Treatment Options
Treatment varies depending on the type, stage, and individual circumstances. Common approaches include:
Includes lumpectomy (removal of the tumor) or mastectomy (removal of the breast).
Uses high-energy waves to kill cancer cells.
Involves drugs that destroy or slow the growth of cancer cells.
For hormone-receptor-positive cancers, this helps block the body’s natural hormones from fueling cancer growth.
Uses drugs that specifically target cancerous cells without affecting healthy cells.
Conclusion
Breast cancer is a serious but often treatable disease when detected early. Education, awareness, and regular screenings are key to reducing risk and improving outcomes. If you notice any unusual changes in your breasts, consult a healthcare professional immediately.

 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer Smoking Cancer
Smoking Cancer Mouth Cancer
Mouth Cancer